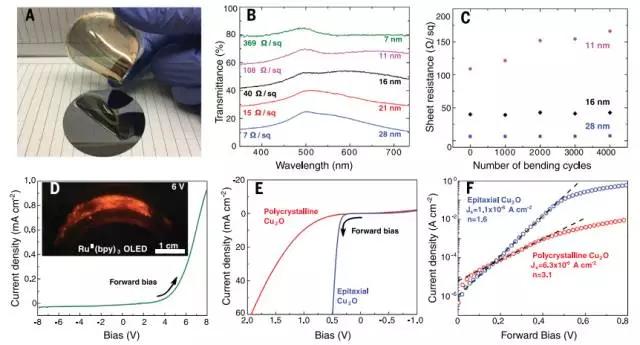
Abstract 1. Epitaxial lift-off ofelectrodepositedsingle-crystalgoldfoilsforflexibleel...
1. Epitaxial lift-off of electrodeposited single crystal gold foil (Epitaxiallift-off of electrodeposited single-crystal gold foils for flexible electronics)
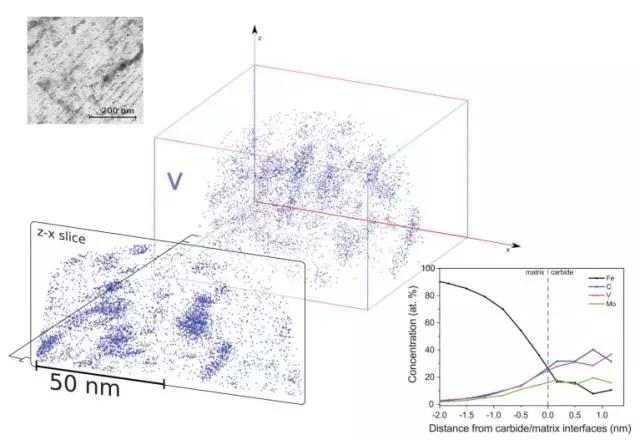
2. Direct observation of a single hydrogen atom at the capture site in ferritic steel
(Directobservation of individual hydrogen atoms at trapping sites in a ferritic steel)
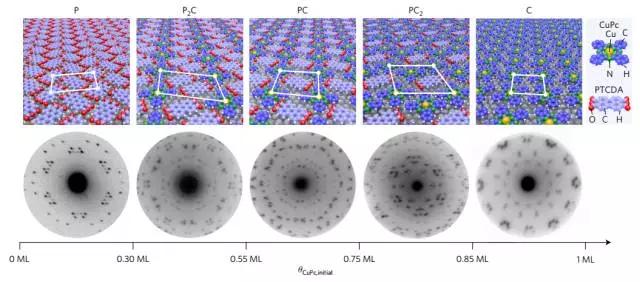
3. Using intermolecular repulsion to control the growth of multiple ordered heterogeneous molecular phases
(Controlling the growth of multiple ordered heteromolecular phases by utilizing intermolecular repulsion)
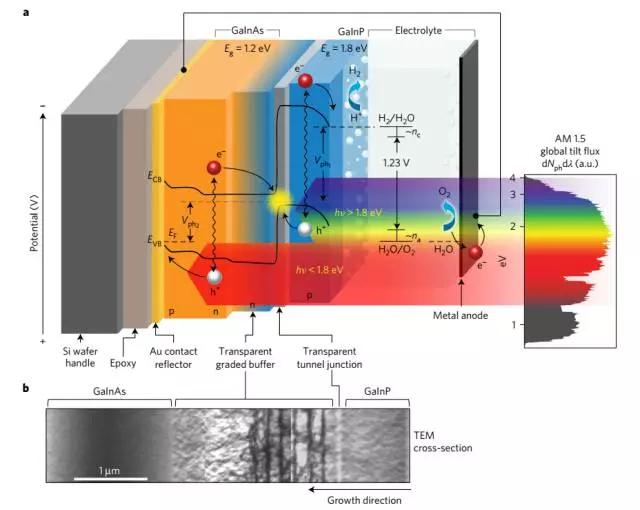
4. Solar energy is directly converted into hydrogen energy
(Directsolar-to-hydrogen conversion via inverted metamorphic multi-junctionsemiconductor architectures)
5. Magnetic polaron on the spin of the dangling bond
(Magneticpolaron on dangling-bond spins in CdSe colloidal nanocrystals)
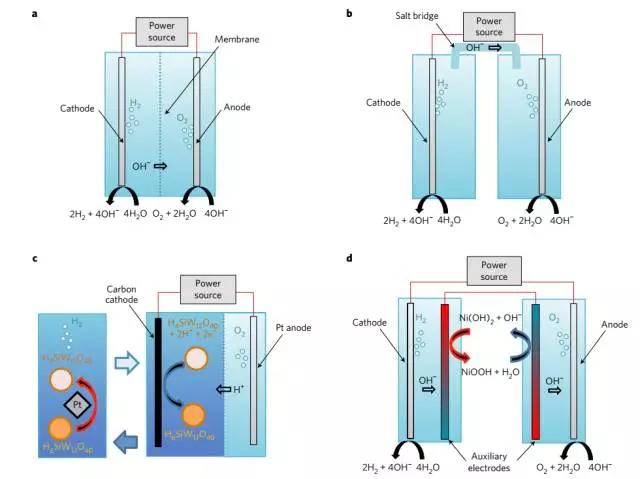
6. Photoelectrochemical hydrolysis in separated oxygen and hydrogen electrolysis cells
(Photoelectrochemicalwater splitting in separate oxygen and hydrogen cells)
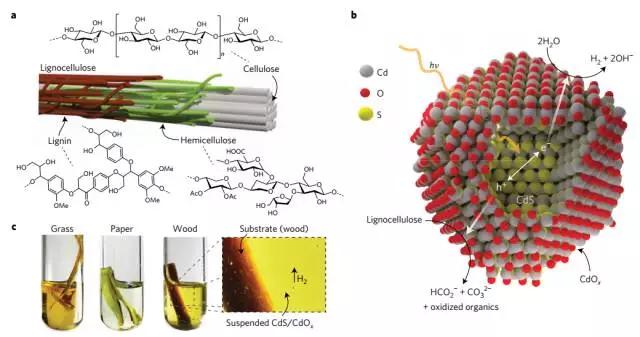
7. Solar driven recombinant lignocellulose into hydrogen
(Solar-driven reforming of lignocellulose to H2 with a CdS/CdOx photocatalyst
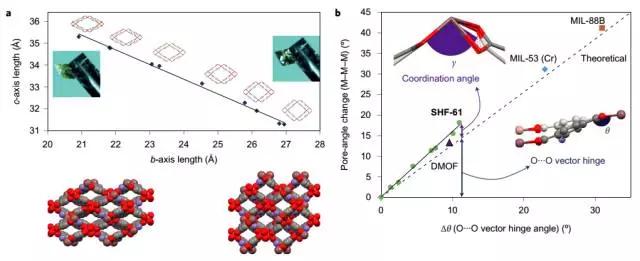
8. Solvent-switchable continuous breathing characteristics and its effect on CO2 vs. CH4 selectivity
(Solvent-switchablecontinuous-breathing behaviour in a diamondoid metal–organic framework and itsinfluence on CO2 versus CH4 selectivity)
Bathroom Hardware Set Including Towel Bar , Towel Shelf, Towel Ring, Toilet Paper Holder, Robe Hook , Soap Holder and Glass Holder can choose.
Bathroom Hardware Set,Bathroom Accessories Simple Set,Stainless Steel Hardware,Bathroom Hardware Accessories Set
Kaiping Jenor Sanitary Ware Co., Ltd , https://www.jmjenorsanitary.com